Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the healthcare industry by enhancing patient care, reducing administrative workloads, and advancing medical research. Currently employed by 79% of healthcare organizations, AI assists human professionals without replacing them. Notable examples include Microsoft’s DAX Copilot, which helps with note-taking and clinical summaries, and augmented intelligence tools that aid in areas like radiology.
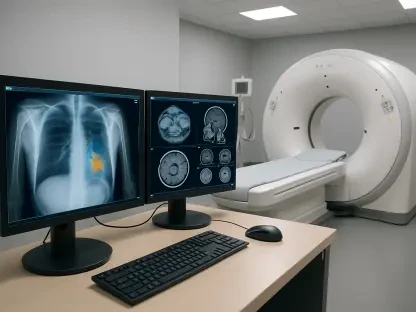
AI shows significant promise in medical diagnosis by analyzing extensive data sets to improve accuracy. Tools like Nuance Communications’ Precision Imaging Network and wearable devices such as Peerbridge Health’s ECG patch facilitate continuous monitoring and early disease detection, leading to timely interventions and better patient outcomes.
In drug discovery, AI accelerates the process by predicting molecular interactions and drug efficacy more efficiently than traditional methods. Technologies like Google’s AlphaFold 3 and Stanford Medicine’s SyntheMol aim to expedite bringing new drugs to market, reducing time and costs.
Patient experience is enhanced through AI-driven chatbots for appointment scheduling and prescription management. Systems like IBM Watson Text to Speech broaden accessibility by supporting multilingual communication. In data management, AI ensures seamless sharing and real-time auditing during Electronic Health Record (EHR) migrations.
Moreover, AI in robotic surgery, exemplified by the da Vinci Surgical System, increases precision in minimally invasive procedures, reducing recovery times and surgical risks.
The healthcare AI market anticipates significant growth, from nearly $27 billion to over $613 billion over the next decade. Future AI applications will likely focus on improving medical training and data security. While AI serves as a powerful adjunct, human expertise remains crucial. AI’s integration promises a more efficient, patient-centered approach to healthcare, offering substantial benefits and transforming the industry.