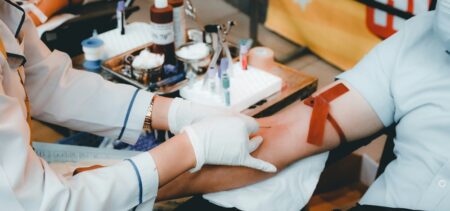
Atrial fibrillation — an irregular and often rapid heart rate — is a common condition that can cause clots to form in the heart that may then dislodge and flow to the brain, potentially leading to a stroke. The standard way to detect these clots requires patients to be sedated and to have a fairly large tube inserted down the throat and esophagus for a transesophageal ultrasound. Investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) have now developed and tested a targeted contrast agent to detect and image these clots noninvasively. They verified the potential of this strategy in a study published in JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging.