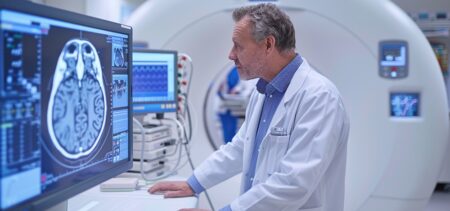
Glioblastoma is an incurable type of brain tumor that is frequently associated with mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). The main EGFR mutation found in glioblastomas, called EGFRvIII, is treated with the antibody mAb806, a drug developed by the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research (US) about 20 years ago, but whose mechanism of action was unknown. In collaboration with the University of Stockholm (Sweden) and the University of California San Diego (USA), researchers at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) have unraveled how this antibody acts on mutated EGFR, thus dramatically extending its application to virtually any glioblastoma mutations.